On August 12, 2026, the sky will offer us one of the most impressive natural spectacles: a total solar eclipse. This phenomenon occurs when the Moon comes between the Earth and the Sun, completely covering the solar disk and plunging certain areas of the planet into a darkness full of mystery and beauty for a few minutes. During this brief moment, which in Catalonia can last up to 1 minute and 37 seconds at the best observation points, the day will turn into night, the temperature may drop slightly, and stars, planets and the solar corona, a halo of incandescent gas that can only be seen during totality, will be visible.
This eclipse will not come alone: it is part of an exceptional trio of solar eclipses that can be observed from the Iberian Peninsula in three consecutive years:
- August 12, 2026: visible as a total eclipse from areas in the north of the peninsula.
- August 2, 2027: with a strip of totality that will cross the south of Spain, especially visible from Andalusia.
- January 26, 2028: annular eclipse visible from Catalonia, with almost total coverage of the solar disk.
This sequence of eclipses is very unusual and represents a unique opportunity for astronomical observation and scientific dissemination.
The totality strip of the eclipse of August 12, 2026 will cross the Arctic Ocean, northeast Greenland and the far west of Iceland, cross the Atlantic Ocean and enter the Iberian Peninsula crossing it from west to east and passing through numerous provincial capitals from A Coruña to Palma, including León, Bilbao, Zaragoza and Valencia.
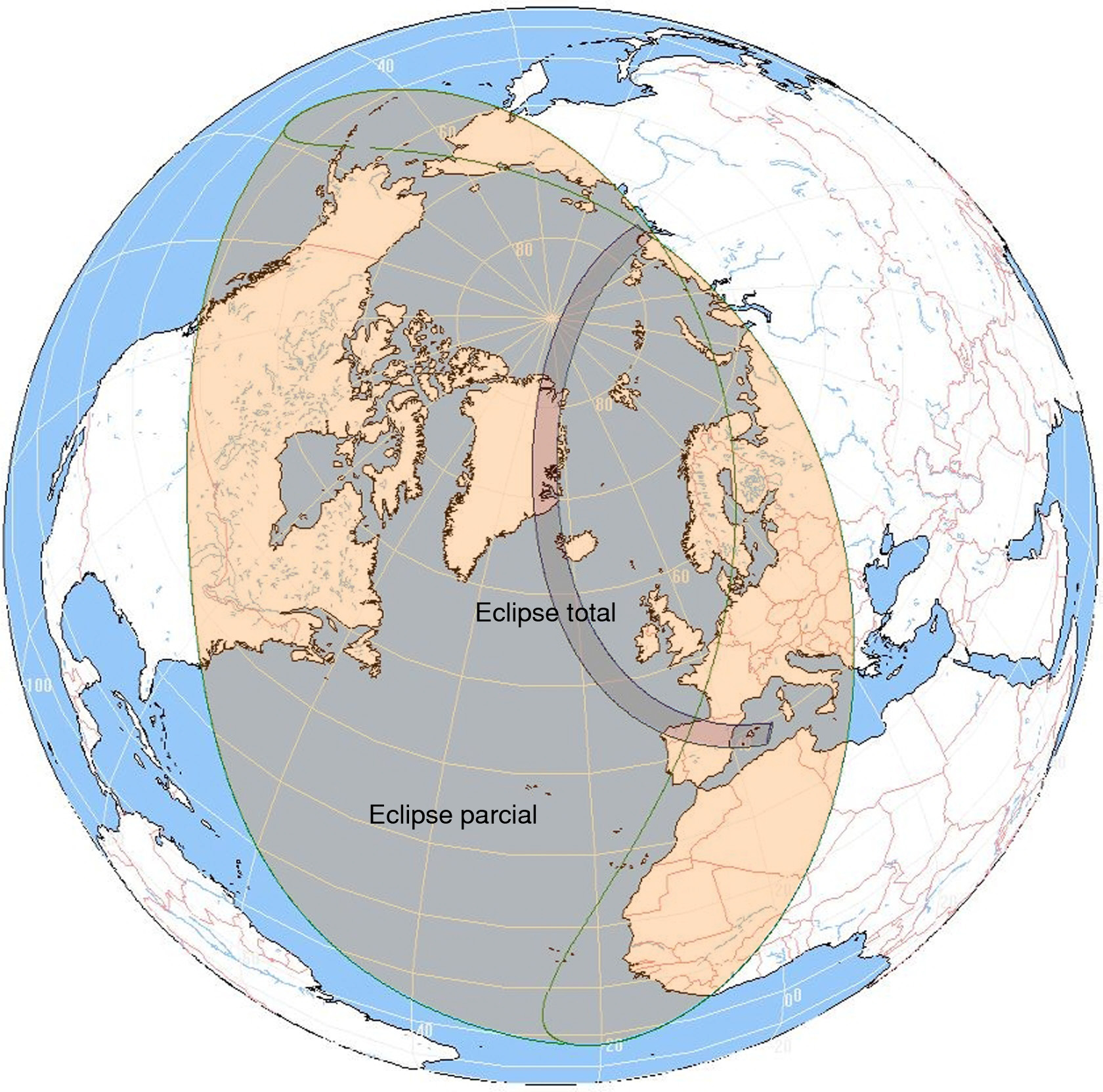
Crèdits: Instituto Geográfico Nacional
Eclipse visibility in Catalonia
Catalonia will play a very special role during the total solar eclipse of August 12, 2026. Although Barcelona and Girona will be outside the zone of totality, cities such as Lleida and Tarragona will be able to enjoy the phenomenon in its maximum splendor, especially in Terres de l'Ebre and the south of Lleida.
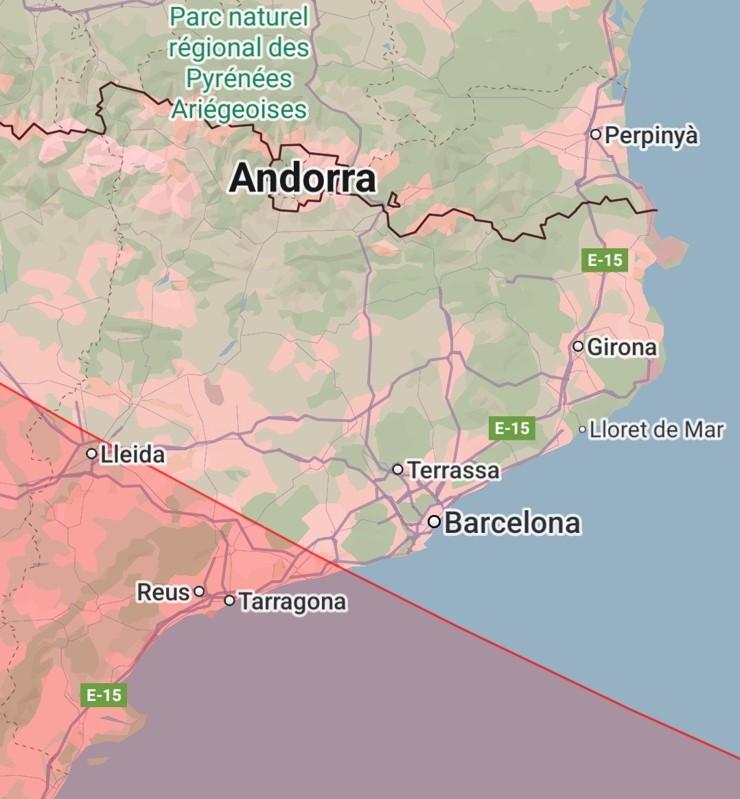
Credit: App Eclipsi Calculator 2.0.
To observe the eclipse well, you must choose a place with clear views to the west to avoid obstacles such as mountains or buildings, since the Sun will be very low during totality.
These places are located within or very close to the totality strip, and offer good observation conditions to the west, which is where the Sun will be during the phenomenon (very low on the horizon).
Recommendation: Choose a high place or with clear views to the west (such as a beach or a viewpoint) to avoid natural obstacles such as mountains or buildings, since the Sun will be very low during totality.
You can check the visibility of the capital municipalities of the region of Catalonia here:
| Municipality | Start of the eclipse | Start of totality | Maximum | End of totality | End of eclipse (sunset) | Duration of totality | Sun height at the maximum |
| Amposta | 19h 36m 13s | 20h 29m 58s | 20h 30m 45s | 20h 31m 31s | 20h 59m 53s | 1m 33s | 4.6° |
| Balaguer | 19h 34m 23s | ---- | 20h 29m 00s | ---- | 21h 01m 09s | ---- | 5.0° |
| Banyoles | 19h 33m 45s | ---- | 20h 27m 55s | ---- | 20h 53m 59s | ---- | 3.9° |
| Barcelona | 19h 35m 01s | ---- | 20h 29m 14s | ---- | 20h 54m 51s | ---- | 3.9° |
| Berga | 19h 33m 50s | ---- | 20h 28m 14s | ---- | 20h 57m 38s | ---- | 4.5° |
| Cervera | 19h 34m 35s | ---- | 20h 29m 04s | ---- | 20h 59m 02s | ---- | 4.7° |
| El Pont de Suert | 19h 33m 20s | ---- | 20h 28m 04s | ---- | 21h 02m 41s | ---- | 5.4° |
| El Vendrell | 19h 35m 19s | 20h 29m 24s | 20h 29m 41s | 20h 29m 57s | 20h 57m 05s | 0m 33s | 4.2° |
| Falset | 19h 35m 29s | 20h 29m 25s | 20h 30m 00s | 20h 30m 35s | 20h 59m 47s | 1m 10s | 4.7° |
| Figueres | 19h 33m 30s | ---- | 20h 27m 38s | ---- | 20h 53m 31s | ---- | 3.9° |
| Gandesa | 19h 35m 39s | 20h 29m 33s | 20h 30m 15s | 20h 30m 57s | 21h 01m 08s | 1m 24s | 4.9° |
| Girona | 19h 33m 59s | ---- | 20h 28m 07s | ---- | 20h 53m 30s | ---- | 3.8° |
| Granollers | 19h 34m 38s | ---- | 20h 28m 51s | ---- | 20h 54m 52s | ---- | 4.0° |
| Igualada | 19h 34m 43s | ---- | 20h 29m 06s | ---- | 20h 57m 28s | ---- | 4.4° |
| La Bisbal d'Empordà | 19h 34m 00s | ---- | 20h 28m 05s | ---- | 20h 52m 34s | ---- | 3.7° |
| La Seu d'Urgell | 19h 33m 24s | ---- | 20h 27m 56s | ---- | 20h 59m 42s | ---- | 4.9° |
| Les Borges Blanques | 19h 34m 50s | 20h 29m 13s | 20h 29m 25s | 20h 29m 36s | 21h 00m 21s | 0m 23s | 4.8° |
| Lleida | 19h 34m 41s | 20h 29m 07s | 20h 29m 20s | 20h 29m 32s | 21h 01m 31s | 0m 25s | 5.0° |
| Manresa | 19h 34m 27s | ---- | 20h 28m 49s | ---- | 20h 56m 57s | ---- | 4.3° |
| Mataró | 19h 34m 44s | ---- | 20h 28m 54s | ---- | 20h 54m 06s | ---- | 3.8° |
| Moià | 19h 34m 18s | ---- | 20h 28m 36s | ---- | 20h 56m 02s | ---- | 4.2° |
| Mollerussa | 19h 34m 39s | ---- | 20h 29m 14s | ---- | 21h 00m 28s | ---- | 4.9° |
| Montblanc | 19h 35m 05s | 20h 29m 18s | 20h 29m 33s | 20h 29m 48s | 20h 58m 53s | 0m 30s | 4.6° |
| Móra d'Ebre | 19h 35m 34s | 20h 29m 29s | 20h 30m 08s | 20h 30m 47s | 21h 00m 24s | 1m 18s | 4.8° |
| Olot | 19h 33m 40s | ---- | 20h 27m 55s | ---- | 20h 55m 14s | ---- | 4.2° |
| Prats de Lluçanès | 19h 33m 59s | ---- | 20h 28m 19s | ---- | 20h 56m 42s | ---- | 4.3° |
| Puigcerdà | 19h 33m 16s | ---- | 20h 27m 41s | ---- | 20h 57m 59s | ---- | 4.6° |
| Reus | 19h 35m 27s | 20h 29m 24s | 20h 29m 54s | 20h 30m 25s | 20h 58m 40s | 1m 1s | 4.5° |
| Ripoll | 19h 33m 39s | ---- | 20h 27m 58s | ---- | 20h 56m 27s | ---- | 4.3° |
| Sabadell | 19h 34m 45s | ---- | 20h 29m 00s | ---- | 20h 55m 27s | ---- | 4.0° |
| Sant Feliu de Llobregat | 19h 35m 02s | ---- | 20h 29m 16s | ---- | 20h 55m 22s | ---- | 4.0° |
| Santa Coloma de Farners | 19h 34m 11s | ---- | 20h 28m 21s | ---- | 20h 53m 52s | ---- | 3.9° |
| Solsona | 19h 34m 01s | ---- | 20h 28m 29s | ---- | 20h 58m 43s | ---- | 4.7° |
| Sort | 19h 33m 19s | ---- | 20h 27m 57s | ---- | 21h 01m 08s | ---- | 5.1° |
| Tarragona | 19h 35m 31s | 20h 29m 25s | 20h 29m 55s | 20h 30m 25s | 20h 58m 01s | 1m 0s | 4.4° |
| Tàrrega | 19h 34m 37s | ---- | 20h 29m 08s | ---- | 20h 59m 31s | ---- | 4.7° |
| Terrassa | 19h 34m 43s | ---- | 20h 29m 00s | ---- | 20h 55m 52s | ---- | 4.1° |
| Tortosa | 19h 36m 03s | 20h 29m 51s | 20h 30m 36s | 20h 31m 22s | 21h 00m 19s | 1m 31s | 4.7° |
| Tremp | 19h 33m 44s | ---- | 20h 28m 24s | ---- | 21h 01m 34s | ---- | 5.2° |
| Valls | 19h 35m 13s | 20h 29m 20s | 20h 29m 40s | 20h 29m 59s | 20h 58m 21s | 0m 39s | 4.5° |
| Vic | 19h 34m 06s | ---- | 20h 28m 22s | ---- | 20h 55m 39s | ---- | 4.2° |
| Vielha e Mijaran | 19h 32m 50s | ---- | 20h 27m 35s | ---- | 21h 03m 05s | ---- | 5.5° |
| Vilafranca del Penedès | 19h 35m 06s | ---- | 20h 29m 26s | ---- | 20h 56m 40s | ---- | 4.2° |
| Vilanova i la Geltrú | 19h 35m 19s | 20h 29m 32s | 20h 29m 37s | 20h 29m 42s | 20h 56m 20s | 0m 10s | 4.1° |
🗺️ Recommended interactive maps: These maps allow you to click on any point in the territory to see local circumstances: start time, maximum, end time, percentage of obscuration (or percentage of the solar disk covered by the Moon), etc.
Instituto Geográfico Nacional map: combines eclipse data with terrain orography data, to indicate the visibility of the eclipse from a specific location.
Credit: Instituto Geográfico Nacional (IGN)
Xavier M. Jubier's map
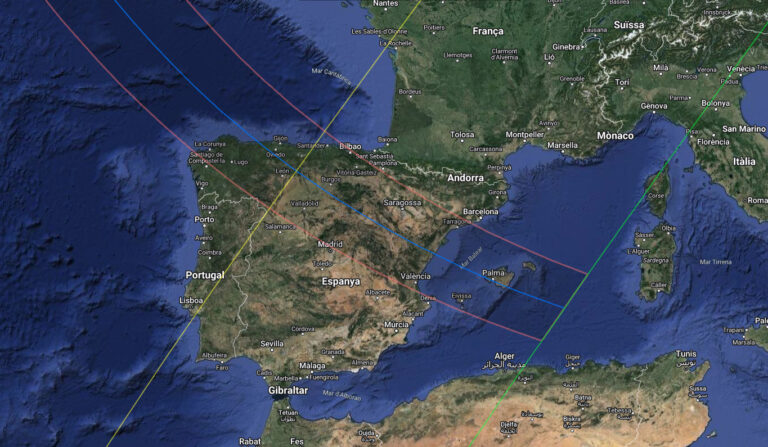
Interactive map with the path of the eclipse of August 12, 2026 (photo: Google Maps). Credits: Xavier Jubier, NASA, Instituto Geográfico Nacional.
Safe observation
Total solar eclipses are spectacular astronomical phenomena, but they must be observed with great caution to avoid irreversible eye damage. During most of the eclipse, part of the solar disk remains visible, and its light can burn the retina without causing immediate pain.
The Sun can only be looked at directly at the exact moment of totality, when the solar disk is completely covered by the Moon. This moment lasts a few minutes and is only visible from the band of totality. Outside this interval, appropriate protection must be used.
Safe methods for observing a solar eclipse:
- Approved eclipse glasses: They must comply with the ISO 12312-2 standard. Conventional sunglasses, or homemade filters such as photographic negatives, CDs or smoked glass, will not work.
- Solar filters for telescopes or binoculars: They must be placed on the objective (never on the eyepiece) and be designed specifically for solar observation.
- Indirect projection: The image of the Sun can be projected through a small hole (pinhole) or with a telescope onto a white surface. This method is safe because you are not looking directly at the Sun.
- Live broadcast: Many observatories and scientific institutions offer online broadcasts of eclipses with expert commentary.
- Important precautions:
- Never look directly at the Sun without adequate protection, not even during a partial eclipse.
- Do not use optical devices (telescopes, cameras, binoculars) without approved solar filters, as they can concentrate sunlight and cause serious injuries.
- Supervise children during observation to ensure they follow safety rules.
📌 General data
| Parameter | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum | 19:45:54 CEST | The moment when the eclipse is deepest and aligned with the center of the Earth. |
| Magnitude | 1,0386 | Proportion of the solar diameter covered by the Moon. If it is >1, it is a total eclipse. |
| Gamma | 0,8978 | Distance (in Earth radii) from the Moon's axis to the center of the Earth. |
| Duration | 2 minutes 18 seconds | The time that the totality phase lasts at the maximum point of the eclipse. |
| Width | 293,9 km | Width of the area of the Earth where totality will be seen. |
| Delta T | 71,3 seconds | Difference between Terrestrial Time and Universal Time (TT - TU). |
| Saros | 126 (48 de 72) | A series of eclipses that repeats every ~18 years. This is number 48 of 72. |
Links of intrest:
- Observatorio Astronómico Nacional
- Comissió Nacional de l'Eclipse (CNE)
- Eclipsophile: Climate and Weather for Celestial events.
- Visualitzador de l'eclipsi total de Sol del 12 d'agost de 2026 a l'Observatorio Astronómico Nacional
- Interactive map Shadepmap
- Interactive map Besselianelements

