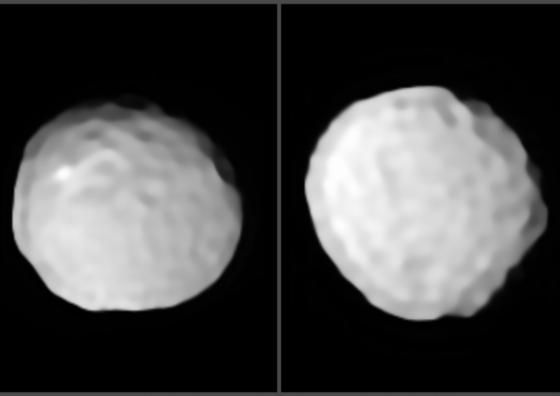
The authors of the study reveal for the first time detailed images of Pallas, including of its cratered surface.
The asteroid Pallas is the third biggest object of the asteroid belt, and was the second one to be discovered in 1802. Since then, several of its features have been described, such as its orbit and its inclination, but several of its details, like the type of surface, origin and radius, remained unknown.
One of the main issues that researchers face when describing certain objects of the Solar System is that the data they have are optical images taken form the Earth. This study combined several of this pictures, taken with the telescope VLT/SPHERE (Very Large Telescope), with 3D models. The VLT is a system of four separated telescopes, placed at the Atacama Desert in Chile. It uses the SPHERE instrument, a system of high-contrast optics devoted to the search and study of exoplanets. The team captured images of Pallas at a point in its orbit that was closest to Earth.
One of the members of the team is Toni Santana-Ros, postdoc researcher in Solar System and Minor Bodies at our Institute. Santana-Ros coordinated the follow-up of the images during the project’s first year. His group processed the light-curve data, which then another team used to build the 3D model. Those models allowed the researchers to reconstruct those non-visible parts of the pictures, and obtain more information.
“Combining both things give us information about certain areas of the object that might remain hidden in the normal pictures, and the 3D model also allows us to scale the objects and calculate certain parameters such as the radius. This time, we calculated Pallas’s density, a measure that was still a matter of discussion among academics”, Toni says.
The team also made two additional observations; an unusually bright spot in the southern hemisphere, and an impact basin in the asteroid’s equator. Researchers concluded that this impact basin is the result of a collision that took place 1.7 billion years ago, caused by an object of 20 to 40km. concerning the bright spot, they suspect that it might be due to the shining of a big salt deposit.
This study provides information about the origin and evolution of Pallas. The researchers have seen that its surface is cratered, which indicates that it has been impacted many times because of its leaning orbit. It is the most cratered object of the asteroid belt.
You can read the press release at the Institute of Cosmos Sciences website, and the original article at the Nature Astronomy journal.